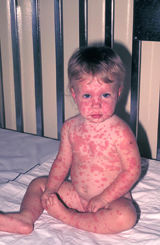
 Erythema multiforme (EM) is an immune reaction to an infection or medication that occurs primarily in children and young adults. It appears as red, target-like lesions, usually on the hands, feet, lips, and genitals.
Erythema multiforme (EM) is an immune reaction to an infection or medication that occurs primarily in children and young adults. It appears as red, target-like lesions, usually on the hands, feet, lips, and genitals.
The center of the patch can form a blister that evolves into a crust-covered lesion within a few days.
Infections are the most common cause of Erythema multiforme, triggering 90% of cases.
The most frequent EM triggers include the virus that causes cold sores (herpes simplex virus 1, HSV-1) and mycoplasma infections (atypical pneumonia).
Medications, such as antibiotics and anticonvulsants may also trigger erythema multiforme.
Treatment
Treatment is directed at controlling the underlying infection or eliminating the suspected offending medication.
Steps are also taken to reduce discomfort and prevent infection of the lesions. Acetaminophen (Tylenol), oral antihistamines, and topical anesthetics (lidocaine) are often recommended, particularly for patients with oral lesions.
Erythema multiforme usually resolves within 2-6 weeks but can recur.
It is often called erythema multiforme minor to distinguish it from a more severe condition called erythema multiforme major (Stevens Johnson Syndrome).
Source: Vivacare
Last updated : 7/17/2022