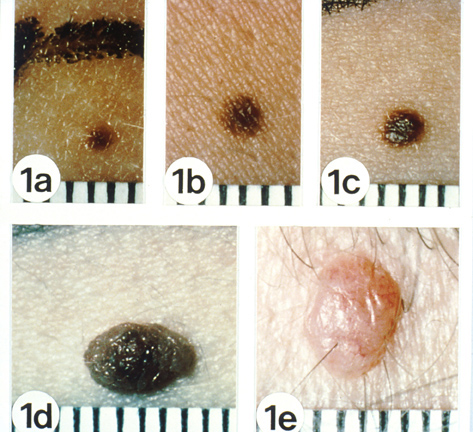
 Moles are very common growths on the skin. Another name for a mole is a nevus. The plural is nevi.
Moles are very common growths on the skin. Another name for a mole is a nevus. The plural is nevi.
Most people have between 10 and 40 moles on their body. They may be pink, tan, brown, or a color similar the person’s normal skin tone.
Although common moles may be present at birth, they usually appear later in childhood. Most people continue to develop new moles until about age 40. Moles may darken during pregnancy or after sun exposure. In older people, common moles tend to fade away.
Moles are usually round or oval and smaller than a pencil eraser.
Moles can be flat or raised. Flat moles are called junctional nevi and raised moles are called compound nevi.
People who have dark skin tend to have dark moles.
These growths are usually found above the waist on areas exposed to the sun. They are seldom found on the scalp, breast, or buttocks.
What causes moles?
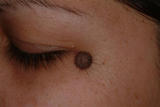
Melanocytes produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes produce more pigment, causing the skin to tan, or darken. Sometimes, clusters of melanocytes and surrounding tissue form noncancerous growths called moles. (A mole is also called a nevus, or the plural, nevi.)
A halo nevus occurs when the skin surrounding a mole loses its pigmentation or color. This is benign and often the central mole and white ring will disappear with time. Halo nevi are most common in children and teenagers.
Most moles are harmless and do not require treatment. When moles are surgically removed, they normally do not return.
Can a mole turn into melanoma?
Yes, but a common mole rarely turns into melanoma, which is the most serious type of skin cancer.
Although common moles are not cancerous, people who have more than 50 common moles have an increased chance of developing melanoma.
People should tell their doctor if they notice any of the following changes in a common mole:
- The color changes
- The mole gets unevenly smaller or bigger (unlike normal moles in children, which get evenly bigger)
- The mole changes in shape, texture, or height
- The skin on the surface becomes dry or scaly
- The mole becomes hard or feels lumpy
- It starts to itch
- It bleeds or oozes
Everyone should perform a monthly skin self-exam. This is particularly important if you have many moles on your body.
Use a body mole map to keep an inventory of the number moles, their location and appearance. You should make an appointment to see your doctor if you notice a new mole, a change in the size, shape or color of a mole, or find another suspicious skin lesion.
Avoiding sun exposure and using a sunscreen regularly are two basic steps to help prevent moles from developing.
Source: Vivacare
Last updated : 1/8/2019