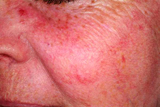
 Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes redness and swelling of the face that can also affect the scalp, neck, ears, chest, and back. Eye symptoms (ocular rosacea) are also reported by half of people with rosacea.
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes redness and swelling of the face that can also affect the scalp, neck, ears, chest, and back. Eye symptoms (ocular rosacea) are also reported by half of people with rosacea.
Those afflicted with rosacea may first notice a tendency to flush or blush easily (facial flushing). The condition progresses to persistent redness, pimples, and visible, threadlike blood vessels (telangiectasias) in the center of the face. These skin changes can eventually spread to the cheeks, forehead, chin, and nose.
Rosacea occurs most commonly in people 30 to 50 years of age. Although women have rosacea more commonly than men, men tend to suffer more severe forms.
Although rosacea's cause remains unknown, it appears to involve a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Rosacea is not contagious.
Rosacea, also called acne rosacea, is different from the acne common in teenagers called acne vulgaris.
Early diagnosis and treatment of rosacea can control symptoms, alleviate discomfort, and stop rosacea from progressing.
Without proper treatment, rosacea tends to worsen and can become disfiguring. Signs that rosacea is worsening include increasing redness, pimples, and/or thickening skin.
Rosacea can be effectively controlled with appropriate medical treatment and lifestyle modifications.
Source: Vivacare
Last updated : 1/8/2019