80% of people with psoriasis will experience scalp psoriasis some time during their lives.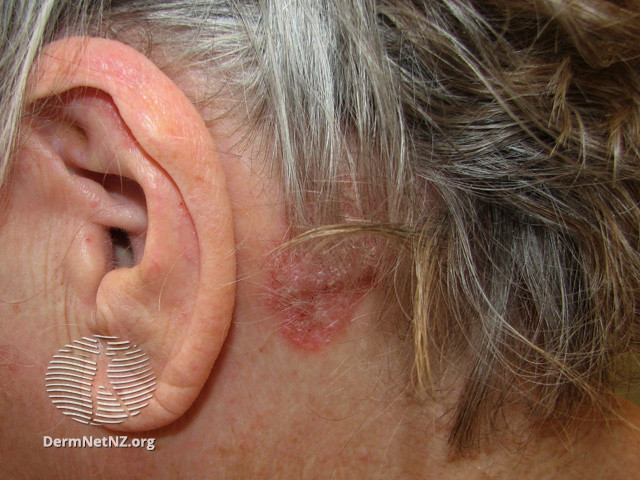
Scalp psoriasis leads to red, irritated areas of the scalp or hairline with silvery-white scales that flake off into the hair or onto the shoulders. It can extend to the forehead, back of the neck, and around the ears.
Severe cases of scalp psoriasis can lead to hair loss. The hair loss results from the accompanying scratching, forceful removal of scales, and stress of the disease rather than the psoriasis itself.
Scalp psoriasis is treatable. Psoriasis medications containing coal tar will treat mild scalp psoriasis and help prevent the outbreak of new psoriasis lesions. These are available in a variety of formulations, including gels and lotions. However, coal tar can leave dark stains, so be sure to protect clothes and bedding.
Topical corticosteroids may be prescribed for cases of scalp psoriasis that do respond to over-the-counter medications. Prescription-strength corticosteroids with clobetasol, such as Clobex® or Olux® , or other potent corticosteroids may be recommended. Solutions and foam formulations can make it easier to apply the medication to the skin beneath the hair.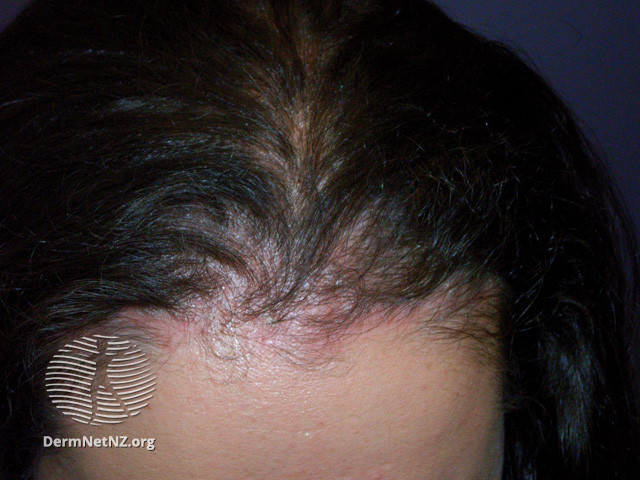
Removing the layers of scale may lead to better results because scale-covered plaques can interfere with absorption of topical medications. Warming the scalp and applying oils, lotions, or creams can loosen the scales, making them easy to remove with gentle combing or brushing.
It is important to remember that you are treating the skin on the scalp and not your hair. It may help to reach the skin by parting your hair in several places and rubbing the medications directly onto the scalp.
For more persistent cases of scalp psoriasis, a regimen of phototherapy or systemic medications, including cyclosporine, oral retinoids (Soriatane), methotrexate, or biologics, may be recommended.
Image Source: DermNet NZ
Source: Vivacare
Last updated : 7/15/2021