Abdominoplasty - This operation is also called a “tummy tuck,” but don’t be fooled by the cute name. Abdominoplasty is a major surgical procedure that flattens the belly by removing excess fat and skin and tightening the underlying muscles. It is best for individuals who have overhanging skin after weight loss that cannot be treated by liposuction alone.
Abscess - An infection that leads to a collection of pus within the tissue.
Ablation - Removal, such as by an ablative laser.
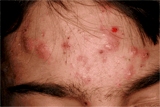 Accutane- Accutane is the brand name for an acne medication that is no longer available, but is still well know. The active ingredient of Accutane®, isotretinoin, is still available in other formulations. Isotretinoin is a derivative of vitamin A. It works by opening pores, dries out the skin by shrinking the sebaceous glands, and probably has some anti-inflammatory benefits as well. Because it comes with potential side effects, ranging from dry skin and chapped lips to depression—and can cause birth defects if you take it while pregnant— is reserved for only the most stubborn, unrelenting cases of acne, including the type of cystic acne that leaves permanent scars.
Accutane- Accutane is the brand name for an acne medication that is no longer available, but is still well know. The active ingredient of Accutane®, isotretinoin, is still available in other formulations. Isotretinoin is a derivative of vitamin A. It works by opening pores, dries out the skin by shrinking the sebaceous glands, and probably has some anti-inflammatory benefits as well. Because it comes with potential side effects, ranging from dry skin and chapped lips to depression—and can cause birth defects if you take it while pregnant— is reserved for only the most stubborn, unrelenting cases of acne, including the type of cystic acne that leaves permanent scars.
Acne is a common skin problem that shows up as outbreaks of bumps, papules and/or pustules often called pimples or zits. Acne lesions usually appear on the face, neck, back, chest, and shoulders. Although most people associate the disorder with teenagers, acne can emerge at any age until menopause, especially during times of hormonal flux.
Acne occurs when excess sebum created by the sebaceous glands, builds up beneath the skin within a hair follicle (“pore”). This creates a small bump called a “comedo”. A comedo may be referred to as a “blackhead” if the sebum has darkened upon exposure to air. The sebum can become infected with bacteria (p. acnes) which causes the lesion to become red and inflamed. The severity of acne is determined by the extent of the lesions and the degree of inflammation.
Acne can be a source of emotional distress and severe acne, particularly “cystic” or “nodulocystic” acne can lead to permanent scars.
Treatment recommendations are based on the severity of the acne and other variables, and may include benzoyl peroxide, topical retinoids (Differin®, Epiduo®, Retin A Micro®, Tazorac®, tretinoin, and Ziana®), dapsone (Aczone®), topical antibiotics (Duac®, Clindagel®), oral antibiotics, birth control pills (Yaz®, Ortho Tri-Cyclen®), isotretinoin (Sotret®), and various laser and light sources, such as photodynamic therapy (PDT).
Acute -A condition that has appeared recently or is of a short duration. The opposite of chronic or long-lasting.
Alexandrite laser - This is a reliable device for removing hair and unwanted pigment spots like freckles, moles, and brown birthmarks.
Allergen - A substance that triggers an allergic reaction in people who are sensitive to it.
Alopecia -Hair loss.
Alopecia, androgenic -Hair loss in men and hair loss in women from hormonal changes to the hair follicles. In men, it is referred to as “male pattern baldness."
Alopecia areata
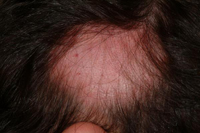
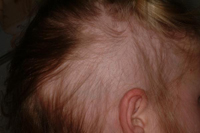
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune and often reversible disease in which hair loss occurs in sharply defined patches, usually involving the scalp or beard. In most cases of alopecia areata, hair falls out in small, round patches about the size of a quarter. In many cases, the disease does not extend beyond a few bare patches. However, in some people, the hair loss is more extensive.
Alopecia totalis -A form of alopecia areata that leads to total hair loss from the scalp and face.
Alopecia universalis -A form of alopecia areata that leads to total hair loss on the scalp, face, and body.
Alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) - This term includes glycolic, lactic, and fruit acids. Blended into topical lotions and chemical peel solutions, these ingredients break down the uppermost layer of skin cells, increasing cell turnover and revealing brighter, younger-looking skin underneath.
Alpha lipoic acid - This is an antioxidant that can help to prevent premature aging of the skin, including the development of fine lines and wrinkles, when it is taken orally or used topically.
Anagen -The growing phase of the hair follicle. Each hair follicle goes through a growth phase (anagen) that last several years, before a resting phase (telogen) that last several months. Finally there is the declining phase (catagen).
Antioxidant - By preventing free radicals from damaging and aging healthy skin cells, this ingredient can stave off some aspects of sun- induced skin aging, such as wrinkles and brown spots. It can also potentially reduce the risk of skin cancer. Some of the most promising antioxidants include idebenone (which is in the cream Prevage), coenzyme QlO, vitamins C and E, and botanicals like soy, green tea, malic acid, and pomegranate. Studies show that consuming these ingredients orally might help your skin even more than applying them topically.
Artefill® - This filler is made from microspheres of polymethyl methacrylate (or Lucite) suspended in bovine (cow) collagen. The collagen is absorbed by the body after two to four months, leaving behind tiny spherical beads that last forever. This makes Artefill one of the truly permanent fillers.
Atopic Dermatitis -Atopic dermatitis, sometimes referred to as “eczema” is a chronic skin disorder that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. The rash of Atopic dermatitis comes and goes in cycles. The worsening of atopic dermatitis (“flares”) can be brought on by a variety of triggers.
Atopy (atopic) -A genetic predisposition to the development of hypersensitivities, including allergies, and asthma.
Atrophy -A decrease in the volume of tissue. Atrophic skin is thin and may appear slightly sunken.
Autoimmune disease -A disease that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues ("auto" means self). Examples include rheumatoid arthritis and bullous pemphigoid.
Basal cell -A type of skin cell found in the lowest levels of the epidermis. These generate new skin cells (keratinocytes) that grow to the surface of the skin.
Benzoyl peroxide -A topical medication that is commonly used to treat mild acne, or in combination with other medications for the treatment of moderate acne. This popular medication works by opening biackheads and whiteheads and killing the bacteria that cause pimples. Although benzoyl peroxide can be harsh and drying in some skin types, it can be very effective for getting rid of existing pimples.
Brand names include Clearasil®, Proactiv®, and Benzac®. It is especially effective when used with a topical retinoid (Differin®, Retin A Micro®, Tazorac®, tretinoin) and a topical or an oral antibiotic. Some formulations combine a topical retinoid with benzoyl peroxide (Epiduo®).
Biologics -Biologics (also called “disease-modifying therapy” or “immunomodulators”) are a relatively new treatment option for people with moderate to severe psoriasis. They are given this name because they are derived from human or animal proteins instead of chemicals like most other medications. They work by targeting specific parts of the immune system. Biologics must be administered by injection, either into the skin (subcutaneously), into the muscle (intramuscular or IM), or by intravenous infusion (IV). Brand names include etanercept (Enbrel®), adalimumab (Humira®), infliximab (Remicade®), and ustekinumab (Stelara®).
Biopsy (skin) -The removal of tissue to diagnose a skin disorder.
Blackhead (see comedo).
Blepharoplasty - Another name for eyelid lift, and one of the most commonly performed invasive cosmetic procedures, blepharoplasty rejuvenates the eyes by removing the excess skin and sometimes the fat that causes drooping of the upper lids. It also often entails removing the fat, skin, and muscles that form bags beneath the eyes.
Blister -An enclosed collection (bubble) of fluid within or beneath the epidermis.
Blue light therapy - This therapy uses a color and wavelength of light to treat inflammatory acne by killing acne-causing bacteria. It is frequently used in conjunction with Levulan, a topical light-sensitizing medication.
Blue nevus -A benign mole with a dark blue color that results from the pigment being in the deep layers of the skin. Seen most often in older children or adolescents.
Blue reticular leg veins - These are flat, painless leg veins that emerge in a netlike pattern, most often in women with fair skin.
Botox® - A commercial form of botulinum toxin manufactured by Allergan that may be used to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and to reduce excess sweating (hyperhidrosis).
Botulinum Toxin - Botulinum toxin is a neuromodulator that causes muscle weakness when very small, diluted doses are injected into the muscle. Several commercial formulations of botulinum toxin are available, including Botox®, Dysport® and Xeomin®. When administered into facial muscles botulinum toxin weakens the tiny facial muscles that are responsible for creases and wrinkles caused by repeated negative facial expressions.
Breast augmentation - This surgical procedure enlarges the size and/or changes the shape of the breasts, usually with implants made of saline, silicone, or, less often, the patient’s own fat. Silicone, which had been taken off the American market until recently—some say inappropriately—is now available again. The choice of saline versus silicone implants is best made in consultation with your surgeon.
Breast reduction - Also known as reduction mammoplasty, this surgery firms, lightens, and reduces the size of very large breasts by removing fat, skin, and sometimes breast tissue.
Brow lift - This surgical procedure helps to rejuvenate the upper face by elevating drooping eyebrows while smoothing the deep lines and furrows in the forehead. (It’s also called a forehead lift.) Some patients opt to have a brow lift with a face-lift and/or blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery).
Bulla -Large blister that measures at least 1cm (0.4 inches) at its widest point. Larger than a vesicle.
Bullae -Plural of bulla.
Bunny lines - These are tiny creases that form along the sides of the nose. They are especially obvious when you crinkle your nose and tend to worsen with age.
Catagen -The declining phase of the hair follicle. During catagen, the hair follicle shrinks. Each hair follicle goes through a growth phase (anagen) that last several years, before a resting phase (telogen) that last several months. Finally there is the declining phase (catagen).
Cellulite - Affecting at least 90 percent of women over the age of eighteen in the United States, cellulite appears when the fat just below the skin begins to pucker between the vertical bands of fibrous tissue that contain it. It’s usually resistant to exercise and is found even in physically fit women who are at their ideal body weight.
Cellulitis -An infection of the skin, usually by bacteria (staph and strep). Learn more about cellulitis.
Chemical peel - Acid peel solutions are designed to remove the upper layers of the skin’s surface and enhance the deeper skin layers. Just how deeply a peel penetrates, and thus how long you need to recover, varies tremendously, from quite superficial to deep, depending on the type of chemical and treatment that you and your doctor choose.
Chronic -Long-lasting. The opposite of acute.
Cleanser - Available in sensitive, foamy, granular, creamy, anti-aging, and oil-zapping varieties, these formulas remove excess dirt, debris, and product residue from the skin. This not only makes the complexion look more radiant but also helps any subsequent products you apply to absorb more effectively.
Collagen - This protein is a major structural component of the skin, the ligaments, the tendons, and the bones. In the skin, it degrades from years of sun damage and age, resulting in yellowing, wrinkling, and sagging. Since the 1970s, dermatologists have been injecting lips, fine lines, and wrinkles with synthetic collagen derived from cattle, sold under the names Zyderm® and Zyplast®, a thicker version. In early 2003, the FDA approved two fillers made of human tissue, Cosmoderm and the thicker Cosmoplast. Unlike bovine collagen, the latter two don’t cause allergic reactions; thus skin tests prior to treatment are unnecessary.
Comedo -A dilated hair follicle and sebaceous gland filled with sebum and bacteria. A comedo may be "open" in which the sebum is exposed to the air causing the sebum inside to turn dark or black. This is referred to as a “blackhead.” A comedo may be “closed” in which the sebum inside remains white. This is referred to as a “whitehead.”
Comedones -Plural of comedo.
Compression sclerotherapy - One of the most popular and effective treatments for big, ropy veins, this variation on traditional sclerotherapy entails wrapping the legs in pressure stockings for two or three days after the injection.
Corticosteroids -Corticosteroids are a family of medications used to control inflammation. Different from the “steroids” (anabolic steroids) used by athletes and body builders. May be taken by mouth (prednisone) or applied topically to the skin (1% hydrocortisone cream).
Topical corticosteroids may be ranked on their strength. Group 1 (I) corticosteroids are "super potent" and have the greatest risk of side effects if used for prolonged periods. Group 7 (VII) corticosteroids are “low potency” and include 1% hydrocortisone that can be purchased over the counter.
Cosmeceutical - This is a hybrid product that straddles the line between a cosmetic and a pharmaceutical prescription.
Cosmetic surgery - With an increasing number of minimally invasive treatments available in the dermatologist’s office, it’s become harder and harder to define just what cosmetic surgery is. Face-lifts and breast augmentation are two obvious examples, but injectable fillers, Botox, and lasers come under this category, too. The last three prove that you don’t have to go under the knife, empty your bank account, or spend months of recovery time to see a spectacular change in your appearance.
Cryotherapy - A cold substance, such as liquid nitrogen, is used to remove skin lesions.
Dermal filler - A substance injected into the dermis to give the skin a fuller look.
Dermatitis -A general term used to describe inflamed skin. There can be many causes of dermatitis, such as an allergic reaction or atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis can be short-term ("acute") or long-term ("chronic"). Acute dermatitis causes the skin to appear red, blistered or swollen. Chronic dermatitis causes the skin to appear thickened, rough, and darker than the surrounding skin.
Dermatology -The medical specialty focused on the diagnosis and treatment of people with skin conditions (including hair and nails).
Dermatologic surgery -The diagnosis, treatment and repair of clinical and cosmetic problems of skin, hair, nails, and other tissues by surgical and non-surgical methods. Procedures include laser surgery, cryosurgery, excision, Mohs surgery, dermal fillers, and hair restoration. Also called dermasurgery.
Dermatophyte -A fungi that lives on the top layer of the skin. Found on all people, including those with normal skin. May overgrow, leading to problems such as athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) or tinea versicolor.
Dermis
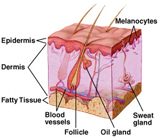
The deep layer of skin that lies below the epidermis. Contains collagen, blood vessels, nerves, sweat glands (eccrine glands), and sebaceous glands.
DMAE - This stands for dimethylaminoethanol, a substance found naturally in fish. Some people believe that it boosts brain power when it is taken orally. Rubbed on topically, it can tighten the skin, at least temporarily.
Elastin -A protein found in the dermis layer of skin that provides skin with its elasticity. The loss of elastin, as occurs with aging, leads to skin that loses its shape.
Electrodessication and curettage (ED&C) -The removal of skin growth with a rounded knife (curette). The wound is heated to prevent bleeding. May be used to treat certain types of skin cancer or precancerous lesions. A local anesthetic is injected before the procedure.
Endoscopic brow lift - In this less invasive alternative to the traditional brow lift, a surgeon makes four to six tiny incisions in the scalp, slips a stainless-steel viewing probe under the skin that will allow him or her to pull sagging areas taut, and sometimes even snips some of the muscles that cause frown lines. The recovery time and postoperative numbness is generally far less with the endoscopic procedure, but the lift tends to be less pronounced and the results shorter-lived.
Epidermis -The top layer of skin that lies above the dermis.This is the tough, protective outer layer of skin. Its main purpose is to protect the body from external toxins, poisons, germs, and injury.Epidermis is composed primarily of a type of squamous cell called a keratinocyte. Cells at the base of the epidermis (basal cells) generate keratinocytes that grow to the surface. The epidermis replaces itself every 12-14 days. There are no blood vessels in the epidermis so a cut or scrap of the epidermis does not bleed.
Erysipelas -A type of cellulitis.
Erythema -Redness of the skin that is greater than the surrounding skin. May be a sign of inflammation from flushing, infection, sunburn, or other conditions.
Exanthem -An acute rash that results from an infection, particularly viruses.
Excision -The removal of a skin growth with a scalpel. The wound is usually closed with stitches. If done for purposes of a biopsy, the tissue may be sent to a laboratory for further examination under a microscope.
Exfoliant - This is the name for any cleanser or treatment that physically or chemically removes the uppermost layer of skin cells to reveal younger, healthier, and more radiant skin underneath. Scrubs, microdermabrasion, vibradermabrasion, and acid peels all fall into this category.
Exfoliation -The removal of the top layer of skin. This may occur naturally as the result of a skin disease, such as sunburn. Or it may result from an elective procedure such as dermabrasion or microdermabrasion.
Face-lift - This surgical procedure redrapes the skin to cover the lower part of the face and neck by cutting out excess skin and sometimes fat as well. Less common is the mid-face-lift, which tightens sagging skin in the central portion of the face. Both procedures leave scars and require a healing phase that can range from a few weeks for a minimally invasive face-lift to several weeks for a full face-lift.
Filler - A cosmetic filler is a soft material that is injected into unwanted folds, creases, and wrinkles. It makes them invisible until the material is absorbed into the body. Depending on which filler you use, it lasts between three months and virtually forever. Doctors categorize fillers by their ingredients and their longevity. The major temporary fillers consist of collagen, hyaluronic acid (Juvederm®, Restylane®, Perlane®), hydroxylapatite (Radiesse®), or poly-L-lactic acid (Sculptra®). Permanent fillers are made of methyl methacrylate and silicone. Fillers can be used to augment the lip lines and the lips themselves, to fill creases and lines around the mouth, and to address the volume loss that naturally occurs with aging.
Fitzpatrick type -A scale used to measure the darkness of skin. Fitzpatrick type I describes someone who is pale, with very little skin pigment, who easily sunburns. Fitzpatrick type IV describes someone who is dark with a lot of skin pigment who easily tans when exposed to sunlight.
Folliculitis -The inflammation of one or more hair follicles, usually due to a bacterial infection.
Fractional lasers - This class of lasers, which includes the Fraxel®, Fractional C02, Active FX®, and Profractional, rejuvenates the skin by resurfacing only a fraction of the skin with each treatment, leaving the surrounding areas intact for faster healing and fewer side effects.
Furunculosis -Also known as boils, acute collections of pus, or abscesses arising from several hair follicles and surrounding tissue.
GABA - This stands for gamma-aminobutyric acid, a neurotransmit— ter in the body that makes muscles relax. Used topically, the ingredient can help to soften the facial muscles, thus temporarily smoothing the skin.
Hair bulb -A bulbous collection of actively growing cells at the base of a hair follicle that constantly produces a strand of hair.
Hair follicle -The part of the dermis from which hair grows. Sebaceous glands are often connected to hair follicles.
Hair transplantation - A procedure that uses the patient’s own hair to fill in thinning or bald areas on the scalp. Although many people still associate it with unsightly plugs, the treatment has been revolutionized in the past decade. Individual hairs or clusters of a few hairs are transplanted into tiny slits in the scalp so that even I can’t always tell a transplant job from the real thing. Traditionally used for men with thinning scalps, this is a highly effective treatment for hair loss in women as well.
Halo nevus -A mole with a white ring, or halo, around it. Relatively common and usually seen in children. For reasons still unknown, the immune system starts to recognize the mole as abnormal and leads to changes in the pigment of the surrounding skin. Rarely malignant (cancerous), although it should be examined carefully.
Hives -(see urticaria)
Hyaluronic acid - This spongy material is present in the skin’s dermis (or second layer). It helps to hold collagen and elastin together, giving the skin support and body. Since it attracts water, hyaluronic acid functions as an excellent moisturizer and temporary skin plumper when it is added to topical lotions and creams. Injected into the skin in the form of highly versatile hyaluronic fillers, like Restylane®, Perlane®, and Juvederm®, it smoothes lines, wrinkles, and creases.
Hydrocortisone -A low-potency topical corticosteroid used to treat skin inflammation. Available in 1% formulations without a prescription.
Hydroquinone - This drug is used to bleach away freckles, sun- induced brown spots (lentigines), and melasma. It is available in over- the-counter cosmeceuticals as a 2 percent formulation, but it’s even more effective in the prescription cream Tri-Luma®, which combines a 4 percent hydroquinone solution with Retin-A and a topical steroid. The FDA is considering removing hydroquinone from the market, based on circumstantial evidence that it might be carcinogenic. It has been unavailable in Europe for years.
Hyperpigmentation -An area that is darker than the surrounding skin.
Hypopigmentation -An area that is lighter than the surrounding skin.
Imiquimod -A prescription medication applied to the skin that is FDA approved for the treatment of actinic keratoses (AKs), superficial basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and external genital warts (EGW). It works by activating the body's own immune system. When imiquimod is applied to the skin, immune cells are activated and travel to the area. Zyclara® is the brand name of a form of imiquimod.
Immune system -A complex network of specialized cells and organs that work together to defend the body against "foreign" invaders such as bacteria and viruses. In some conditions, the immune system may not function properly and may even work against the body. This leads to “autoimmune” diseases, such as arthritis and lupus.
Infrared laser - This includes skin-rejuvenation devices like the Smoothbeam, CoolTouch, and Aramis lasers, which stimulate collagen production, thus helping to improve wrinkled and acne-scarred skin. An infrared laser can also minimize acne by temporarily shrinking the sebaceous glands.
Intense pulsed light (IPL) - This tool is not a laser but rather a device that flashes powerful pulses of broad-spectrum light onto the skin to treat a variety of issues. Intense pulsed light can stimulate collagen production, resulting in smoother, less-wrinkled, younger-looking skin. It can also remove unwanted hair, cause sun-induced brown spots to fade, and reduce redness and facial red blood vessels.
Kinetin - A plant-derived hormone found in quite a few cosmeceutical creams, kinetin has long been billed as a nonirritating alternative to retinoids that can help to repair damaged skin cells and protect them from further injury.
KTP laser - This device emits a beam of green light that makes blood vessels invisible and removes sun-induced brown spots from the skin. It is a great tool for easing facial redness, broken facial blood vessels, flushing, and red birthmarks as well as for evening out skin color from sun damage.
Laser - An acronym for “light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation,” this class of devices uses a powerful beam of light to selectively alter the skin. Depending on the technique and the wavelength of the light, a laser device can remove hair, decrease the visibility of red vessels, even out pigmentation, smooth wrinkles, or tighten skin. Ablative lasers, which are used to smooth wrinkles and acne scarring, wound the skin to some degree, causing a variable amount of crusting, scabbing, and redness. Nonablative lasers, which are used to decrease skin redness, brown discoloration, and sagging and to remove hair, do not wound the surface of the skin and therefore require little or no healing time.
Laser skin resurfacing - This treatment removes much of the skin’s wrinkled, scarred, and/or splotchy upper layers, revealing clear, baby- smooth skin underneath. Until recently, the mighty CO2 was our only option for resurfacing. Although it can make you look at least a decade younger in two weeks, it comes with more than a week of recovery time. Now we have gentler resurfacing devices at our disposal, like the Fraxel®, Fractional GO2, Active FX, Pearl, and the Portrait plasma. All are gentler, often necessitating multiple treatments, but require far less downtime than the traditional CO2 laser.
LED photomodulation - Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) painlessly stimulate collagen production. After several treatments, some patients notice that their skin looks smoother and creamier, less red, and more even in color, although the changes are usually extremely subtle.
Leg-vein stripping - This is a popular surgical procedure for varicose veins that, until very recently, required incisions to be made in the skin at intervals along the length of the vein; small portions of the vein were then extracted. It was usually done under anesthesia and left scars at each incision. Many dermatology offices have replaced this treatment with ambulatory phlebectomy, a less invasive procedure that uses tiny incisions to gently extract small fragments of the vein, or endovenous vein removal, an even less invasive technique in which an ultrasound guided laser or a radio-frequency probe zaps the walls of large veins.
Lentigo - This is the medical term for a sun-induced brown spot on the skin. Lentigines accumulate primarily on the face, the hands, the arms, and the legs with age, especially in those who chronically expose themselves to sunlight and tanning beds.
Liposuction - This body-sculpting procedure is best for, but not limited to, those who are already close to their ideal weight but have areas of fat that just won’t budge. It works best when performed on “love handles,” saddlebags, the upper arms, the lower abdomen (below the belly button), the buttocks, the neck, and (for men and even some women) the breasts. Done properly, the outpatient operation removes areas of unwanted fat with minimally invasive techniques and limited anesthesia. Liposuction is not a weight-loss treatment, nor does it cure cellulite.
Long-pulsed diode laser - This laser device uses a beam of light to remove hair and reduce the visibility of large facial blue veins and some leg veins. Because of its long pulse duration, it’s safer on darker skin types than many other lasers are.
Macule -A flat spot that appears different from the surrounding skin. Measures no more than 1cm (0.4 inches) at its greatest diameter. Smaller than a patch.
Malassezia furfur -The fungi that causes tinea versicolor. Another name for Pityrosporum folliculitis.
Melanin -The pigment in skin, created by melanosomes, that gives skin its color. Increases when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation (UV rays).
Melanocytes -The cells in the dermis that create melanin.
Melolabial folds - These creases run from the outer corners of the lips to the chin. They are also known as marionette lines.
Mesotherapy - Primarily used for fat reduction and the removal of Cellulite, this treatment involves the injection of substances that are designed to melt away fat. However, these substances are not regulated, are not approved by the FDA, and have not been properly studied, so patients have no way of knowing how safe or effective they are. The Brazilian government recently banned mesotherapy. This is not an encouraging sign, because Brazil rarely bans anything.
Microdermabrasion - This method uses a fine spray of aluminum oxide or salt crystals to gently sandblast the skin, revealing a, brighter, rosier, younger-looking complexion. Microdermabrasion that is administered or supervised by a doctor tends to be (but isn’t always) more aggressive than the spa procedures performed by aestheticians.
Mohs surgery -A specialized surgery that removes a tumor (or other lesion) in stages. Each portion of removed tissue is examined under a microscope to make sure that cancerous cells have been removed while sparing as much normal skin as possible.
Nasolabial folds - These creases run from the sides of the nose to the mouth and tend to deepen with age.
Nd:YAG laser - A short-pulsed Nd:YAG laser is used to treat lentigines (sun-induced brown spots) and tattoos, whereas the long-pulsed kind is used to remove excess hair in all skin types and to zap unwanted leg veins and blue facial veins.
Nevi -Plural form of nevus.
Nevus -A mole.
Nodule -A round, raised lesion on the skin that measures at least 1cm (0.4 inches) at its greatest diameter. Larger than a papule. If filled with fluid, referred to as a bulla. If flat, referred to as a plaque.
Onychomycosis -A fungal nail infection (usually the large toe) or (less commonly) the fingernails.
Papule -A raised lesion on the skin that measures no more than 1cm (0.4 inches) at its greatest diameter. Smaller than a nodule or plaque. Referred to as vesicle if filled with fluid.
Patch -A flat spot that appears different from the surrounding skin. Measures more than 1cm (0.4 inches) at its greatest diameter. Larger than a macule.
Pathology (dermatopathology) -The examination of tissue under a microscope or with other tests to determine the underlying cause of a condition, define the borders of a lesion, or measure the response to treatment.
Peptide - Popular in cosmeceuticals, this tiny chain of amino acids can prompt the skin cells to make more collagen, the epidermis to normalize, and the blood vessels to become plumper and healthier—all of which should, in theory, reduce the signs of aging over time. Another emerging class of peptides temporarily relaxes the facial muscles that are responsible for crinkling, so the skin looks smoother and fine lines are less obvious. Copper peptides can cause brown spots to fade and smooth wrinkles very slightly.
Photoaging -The aging of skin that is accelerated from exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UV) rays from sunlight or tanning booths.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) - For this combination therapy, which is used to treat acne and the early stages of skin cancer and to rejuvenate maturing skin, dermatologists start by painting a light-sensitive substance called Levulan onto the skin. Then they expose the area to a pulsed dye laser, intense pulsed light, or blue light. Levulan makes these devices far more effective than when they are used alone.
Photorejuvenation - This term refers to the use of light and energy sources, like lasers, intense pulsed light, and radio-frequency devices, to reduce or eliminate unwanted pigmentation, fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging areas of the skin.
Phytophotodermatitis -A rash that appears when sunlight strikes skin that has been sensitized by contact with certain plant materials. For instance, lime juice can sensitize the skin so that exposure to sun leads to a rash where the juice made contact.
Pityrosporum folliculitis -The fungi that causes tinea versicolor. Another name for Malassezia furfur.
Plaque -A flat, raised lesion on the skin that measures at least 1cm (0.4 inches) at its greatest diameter. Referred to as a nodule if rounded or dome-shaped.
Portrait plasma - This resurfacing device zaps the skin with a high- energy nitrogen gas, leaving a paper-thin crust that acts as a protective dressing. The treatment can be very gentle, leaving no wound at all and requiring no healing whatsoever, or progressively more aggressive. With more aggressive treatments, once the “dressing” falls off (after a week or so), you’re left with a fresh, younger-looking complexion that is smoother and more even in color.
PPX system - Also known as Isolaz, this painless treatment uses gentle suction to open and unclog the pores, clean out sebum, expose the skin to intense pulsed light, reduce skin inflammation, and kill pimple- causing bacteria. The treatment is very effective for blackheads, larger blemishes, and, occasionally, cystic acne. It is also used for hair reduction and photorejuvenation.
Pruritus -Itching. The sensation that creates the desire to scratch or rub.
Pulsed dye laser - This is the first laser that was developed specifically for medical use, about twenty years ago, and it has been improved continually since then. The pulsed dye laser is still the treatment of choice for port-wine stain birthmarks. The latest, enhanced version is also one of the most effective tools we have for treating facial blood vessels, redness, flushing, stretch marks, and scars.
Pustule -An elevated lesion, similar to a vesicle, that contains the remnants of the body’s dead white blood cells (“pus”).
Q-switched laser - This is a highly effective, ultra short-pulsed laser that treats brown spots, birthmarks, and tattoos with minimal discomfort. The alexandrite, ruby, and Nd:YAG are examples of Q-switched lasers that are used in skin treatments.
Radiesse - This thick filler (whose generic name is calcium hydroxylapatite) is made from microspheres of a synthetic version of the material found in bones and teeth. Once the spheres are injected, the body slowly produces collagen around them. This filler, which lasts a year or longer, is especially helpful for nasolabial and melolabial folds and for filling hollow cheeks.
Red facial blood vessels - These painless veins that become visible along the sides of the nose and cheeks will worsen with age, especially in fair-skinned individuals, but also in those who smoke, consume alcohol regularly, and expose their skin to excessive sun and heat. These vessels are easily treated with a series of pulsed dye laser or KTP laser sessions or with intense pulsed light.
Retinoids
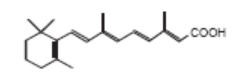
Retinoids are a class of medication derived from vitamin A that are used to treat a variety of skin conditions. Retinoids may be taken orally or applied onto the skin. Isotretinoin (Sotret®) is an oral retinoid used for the treatment of acne. Acitretin (Soriatane®) is a oral retinoid used for the treatment of psoriasis. Several topical retinoids have become the mainstay of treatment for acne, including Differin® (adapalene), Epiduo® (adapalene + benzoyl peroxide), Retin-A Micro® (tretinoin), Tazorac® (tazarotene), tretinoin, and Ziana® (tretinoin + clindamycin). Tazorac® (tazarotene) is also used for the treatment of psoriasis. Renova® and other topical retinoids may also be used for the treatment of aging skin. The retinoid helps to generate healthier, plumper skin cells that create a complexion with fewer fine wrinkles.
Retinol - A weaker cousin to the retinoid, this nonprescription, over- the-counter ingredient helps to speed cell turnover and possibly generate collagen, making the skin look smoother and more even in color over time.
Ringworm -A fungal skin infection caused by a dermatophyte. Similar fungi may cause athlete’s foot or jock itch. Ringworm is not caused by a worm.
Rosacea
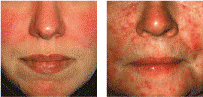
Rosacea is a skin disorder, formerly known as “acne rosacea” that is characterized by flushing, erythema (redness), visible blood vessles (telangiectasias), and papules and pustules on the skin. There are several types of rosacea that are defined by the skin’s appearance. There is also a form of rosacea that affects the eyes (ocular rosacea).
The pimples and pustules of rosacea respond to topical medications, such as MetroGel® and Finacea®, and to oral treatments, such as Oracea® (doxycycline). Several of these medications are used for their anti-inflammatory effects. The redness (erythema) and the visible blood vessels of rosacea ay require treatment with laser or light therapy, such as intense pulsed light (IPL).
Sclerotherapy - The treatment of choice for most leg veins, this procedure entails injecting glycerin, saline, or another medical sclerosing agent into visible veins to safely irritate the vessel wall, causing it to collapse and shrivel up.
Sculptra® - Made from absorbable suture material, this injectable filler (whose generic name is poly-L-lactic acid) is used for facial contouring and to smooth deep lines, hollows, and depressions. Sculptra® stimulates collagen production, so you generally require a minimum of three treatments, spaced one month apart, to see lasting results.
Sebaceous gland -The glands in the dermis that produce sebum, an oily secretion the lubricates the skin. Found most densely on the face, forehead, nose, and upper back (locations where acne most frequently develops).
Seborrhea -Excessively oily skin due to the overproduction of sebum. Increases the risk of acne or seborrheic dermatitis. Sebum -The oil produced by sebaceous glands in the skin. Protects and moisturizes the skin.
Shingles -(see zoster)
Silicone - Used off-label for moderate lines, depressions, creases, and acne scarring, liquid injectable silicone is one of the only truly permanent fillers available.
Skin Cancer -Skin cancer occurs when skin cells start growing abnormally, causing cancerous growths. Most skin cancers develop on the visible outer layer of the skin (the epidermis), particularly in sun-exposed areas (face, head, hands, arms, and legs). They are usually easy to detect by examining the skin, which increases the chances of early treatment and survival.
There are different types of skin cancer, each named for the type of skin cell from which they originate. Basal cell carcinoma (also called BCC) comes from the basal cells in lowest part of the epidermis. 80-85% percent of skin cancers are BCCs. Squamous cell carcinoma (also called SCC) comes from the skin cells (keratinocytes) that make up the top layers of the skin. About 10% of skin cancers are SCC. Melanoma comes from skin cells called melanocytes, which create pigment called melanin that gives skin its color. 5% of all skin cancers are melanoma. Although less common, melanoma is a very dangerous type of skin cancer and is the leading cause of death from skin disease.
Skin Tag -A skin tag is a small harmless, painless, skin-colored growth. It is commonly found on the neck and arm.
Skin type - This describes the qualities of a person's skin, including such individual traits as light vs. dark, dry vs. oily, and other factors.
Skin’s virtual age (SVA) - Unlike your chronological age, your skin’s virtual age refers to the way your complexion looks and feels. Depending on how well you care for your skin, your SVA might be years younger than your actual age, years older, or just about the same.
SmartLipo® - This is a trade name for a type of laser lipolysis, a treatment that combines traditional liposuction with a laser that is designed to melt fat and, some believe, tighten the overlying skin. However, the supposed benefits of SmartLipo, which is considerably more expensive than the conventional version, await proof from properly done studies.
SPF -Used to measure the efficacy of sunscreens, SPF stands for “sun protection factor” and is followed by a number. The higher the number, the more the sunscreen will shield you from UVB rays, which penetrate the skin and cause tanning, burning, and increase the risk of developing skin cancer. The SPF does not reflect how well your sunscreen blocks UVA rays, which penetrate more deeply even through window glass. Exposure to UVA rays leads to premature aging of the skin , as well as some forms of skin cancer.
Spider leg veins - These are tiny red vessels (about the width of a strand of hair) that usually show up on the thighs and upper calves and increase with age. They are best treated with sclerotherapy.
Squamous cell -A type of flat cell forms the surface of the skin, the lining of the hollow organs of the body (such as the bladder, kidney, and uterus), and the passages of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Keratinocytes that form the epidermis are a type of squamous cell.
Staph -Short for staphylococcus, a type of bacteria. A common cause of skin infections, including impetigo and boils.
Sunscreen -This lotion, cream, or spray is the single most important anti-aging weapon you can buy. Sunscreen uses chemicals or physical blockers to prevent a certain percentage of ultraviolet light from getting to the skin and attacking and damaging the skin cells.
In order to guard against both UVA and UVB, you must wear a sunscreen labeled broad spectrum. Most broad-spectrum sunscreens contain the powerful UVA blocker avobenzone. However, since this ingredient breaks down after exposure to sunlight, some companies are stabilizing it with additives like Helioplex®, which dramatically prolong the life span of the sunscreen. The latest UVA blocker to hit the United States is Mexoryl, which remains stable and effective even after four hours of sunlight exposure.
Surfactant - Used to some degree in nearly all soaps and cleansers, surfactants (or detergents) break down and whisk away your skin’s natural oils—and with them, dirt and debris. The more surfactants a cleanser has, the better it works. Thus, depending on how sensitive you are to these cleaning ingredients, a high-surfactant formula could irritate your skin and make it blotchy and flaky. In this case, you should look for a lower-surfactant cleanser.
Steroids -(see corticosteroids)
Stratum corneum -The outermost layer of the epidermis that provides a protective barrier for the skin below.
Strep -Short for streptococcus, a type of bacteria. A common cause of skin infections, including folliculitis and cellulitis.
Tear trough - The sunken area just beneath the inner corners of the eyes. The skin in this region sags as fat redistributes with age, accentuating shadows and the appearance of dark circles and making the face look tired. Eyelid lifting tightens the skin and removes unwanted fat, but only fillers can soften and smooth out the tear trough.
Telangiectasia -Dilated, thread-like blood vessels that appear in the skin as red or dark purple lines. Commonly occur with rosacea, aging, and other skin disorders.
Telogen -The resting phase of the hair follicle. Each hair follicle goes through a growth phase (anagen) that last several years, before a resting phase (telogen) that last several months. Finally there is the declining phase (catagen).
Telogen effluvium -Sudden, diffuse hair loss that occurs when hair is “pushed” prematurely to the resting state of telogen. Possible causes include high fevers, childbirth, severe infections, severe chronic illness, psychological stress, major surgery or illnesses, starvation, and certain medications.
Thermage - This is a tightening procedure that uses radio frequency to heat the deeper layers of the skin. It tightens sagging areas on the face and the body by remolding and firming up the existing collagen and stimulating collagen production. A single treatment is usually all that is required.
Tinea capitis -A fungal infection on the head.
Tinea cruris -A fungal infection in the genital area. Also known as jock itch.
Tinea pedis -A fungal infection of the feet. Also known as athlete’s foot.
Tinea versicolor -A common, unsightly, harmless fungal infection that causes discolored patches on the skin of the back, chest, neck, and upper arms. Caused by pitysporum, also known as Malassezia furfur. Read more about tinea versicolor.
Titan - This infrared light-source device tightens sagging skin by using a deep-heating energy source to remold and tighten collagen below the skin’s surface and stimulate new collagen growth over time. A series of three treatments is usually required.
Topical -Something that is applied to the skin, such as an ointment or cream. A medication to be rubbed over a rash may be referred to as a topical medication.
TriActive - This device combines a laser, suction, and localized cooling to help recontourcellulite dimples.
Trichioracetic (TCA) peel - This medium-depth peel treats lines and pigmentation. After the treatment, your skin will peel off for about seven days, leaving you raw for a week or two longer. TCA peels are still fairly popular; my practice performs quite a few of them. Generally, they require about a week of downtime. On the upside, a single peel makes a huge difference in the quality of the skin, which is a huge plus for those who don’t want to return—or spend the money for—a series of laser or light treatments.
Tumescent anesthesia - Considered a safer alternative to general anesthesia for liposuction, this technique uses a local anesthetic diluted with a salt solution. It is injected into the fat before the fat is suctioned out.
Urticaria -An allergic reaction of the skin. Commonly called hives.
Ultraviolet light (UV) - These are invisible rays of light that come from the sun (and tanning beds), resulting in worrisome changes in skin cells. The two types that dermatologists are most concerned with are UVB, which penetrates the skin, causing tanning, burning, and possibly skin cancer, and UVA, which penetrates more deeply—even through window glass—causing the signs we associate with aging skin (sallowness and wrinkling) as well as some forms of skin cancer. Only a broad-spectrum sunscreen shields you from both UVA and UVB.
UV Radiation -Sunlight is composed of visible light (all the colors we see in daylight), infrared radiation (which provides warmth), and ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which is carcinogenic (cancer-causing).
Varicella -The virus that causes chickenpox. It also may be reactivated years later and cause shingles (see also zoster.)
Varicose veins - These blue, squishable leg veins can be as thick as an adult pinkie finger when they are engorged with blood. Although they’re sometimes painless, they’re often associated with leg aches, especially if you’ve been standing all day. They are best treated with compression scierotherapy, ambulatory phlebectomy, or an endovenous procedure.
VelaSmooth® - This device uses a combination of suction and radio frequency to recontour the dimpling pockets of fat that appear as cellulite Although it’s not a cure, it can be moderately effective in making those pockets less visible and in actual fat reduction.
Vesicle -A small blister that measures no more than 1cm (0.4 inches) at its greatest diameter. Smaller than a bulla. If the lesion has pus but no fluid inside, it is referred to as a papule.
Vibradermabrasion - Like microdermabrasion, this in office proce dure, also known as vibraderm, works by removing layers of dead and damaged skin cells. Because we use textured, gently vibrating paddles to do the job, the resulting redness and swelling are minimal, which makes the procedure an especially good choice for sensitive skin.
Whitehead- (see comedo)
Xerosis -Dry skin.
Zoster -A painful rash due to reactivation of the chickenpox virus, usually years after the initial infection. Commonly called shingles.
Source: Vivacare
Last updated : 5/13/2022