The damaging UV radiation in sunlight can lead to many skin problems, including sunburn, age spots, wrinkles, melasma, freckles, allergic rashes, and precancerous lesions called actinic keratoses.
Most importantly, overexposure to sunlight is the major cause of skin cancer, including melanoma. It is important for everyone to be aware of the damaging effects of sunlight and take measures to avoid overexposure.
Although many people enjoy the appearance of tanned skin and think it looks "healthy," tanned skin is damaged skin. The ultraviolet radiation in sunlight penetrates the deepest layers of the skin where it harms the cells. The body responds by making more pigment (melanin) to try to protect itself, but the damage has already happened and may be permanent. The more exposure you have to the sun, the more likely you are to develop skin problems later in life.
Ultraviolet Radiation
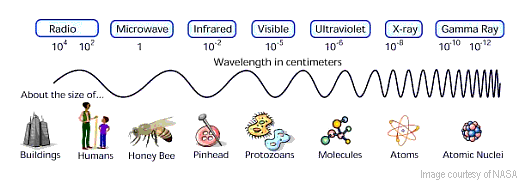
The damaging part of sunlight is called ultraviolet radiation, or UV rays. UV is categorized into three types:
- UVC rays (wavelengths = 200 nm to 290 nm) are the shortest and most powerful of the UV rays. UVC is the most likely to cause cancer if it reaches skin. Fortunately, most of it is absorbed by the ozone layer in our atmosphere. However, there is concern that a thinning of the ozone layer may be causing more UVC to reach the earth's surface.
- UVB rays (wavelengths = 290 nm to 320 nm) are less damaging than UVC, but more of it penetrates to the earth's surface. It is the most common cause of sunburn and skin cancer. UVB is particularly strong at the equator, at high elevations, and during the summer.
- UVA rays (wavelengths = 320 nm to 400 nm) are the least powerful of the UV rays, but they are present all year and can penetrate windows and clouds.
Sun Protection
The first and more effective way to avoid sun damage is to stay out of tthe sun as much as possible.
If you cannot avoid being exposed to sunlight, there are five basic sun defenses that you should keep in mind when you go outdoors:
- Avoid peak hours of sunlight
- Sunscreen
- Clothing
- Sunglasses
- Shade
Avoid Peak Hours of Sunlight (UV Index)

In general, UV rays are the greatest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. It is best to avoid the outdoors during these hours without protection, particularly during summer, in tropical regions, or at altitude. During this time, you should pay close attention to the appropriate use of sunscreen, clothing, sunglasses, and shade.
You can obtain an accurate measure of the amount of UV rays in your area by looking up the Ultraviolet (UV) Index. The UV Index is like a weather forecast. It provides a report on the amount of damaging UV rays that are expected to affect a region on a particular day. The UV Index changes day to day according to time of year, cloud cover, atmospheric ozone, and other factors.
The following table is a breakdown of the UV Index. A high UV Index number means that you are at greater risk of being exposed to ultraviolet radiation. You should take special care to avoid outdoor exposure to sunlight when the UV Index is moderate or greater.
- 0 to 2 = Minimal
- 3 to 4 = Low
- 5 to 6 = Moderate
- 7 to 9 = High
- 10 or more = Very high
The UV Index can be found on our Website or in local papers, usually in the weather section.
Sunscreen
There are several factors to consider when selecting the appropriate sunscreen for proper sun protection.
Sun protection factor (SPF) - Sunscreens are rated by the amount of protection they provide from UVB, measured as the "sun protection factor" or SPF. Sunscreens with higher SPF provide greater protection from the sun. It is best to use sunscreens that offer a minimum SPF of 15.
Broad-spectrum sunscreens - It is best to use a sunscreen that can protect you from both UVA and UVB rays. These are called "broad-spectrum" sunscreens.
Most of the original sunscreens blocked only UVB, but increased awareness of the damage caused by UVA has lead to the development of ingredients that protect against UVA too. Broad-spectrum sunscreens combine ingredients to provide a product with greater protection.
Common sunscreen ingredients that provide protection from UVB rays:
- Cinnamates
- Octocrylene
- PABA (para-aminobenzoic acid)
- Padimate O and Padimate A (Octyl Dimethyl PABA)
- Salicylates
Common sunscreen ingredients that provide protection from UVA rays:
- Avobenzone (Parsol 1789)
- Benzophenones (oxybenzone, dioxybenzone, sulisobenzone)
Sunblocks - "Physical" sunscreen ingredients lie on top of the skin and work by reflecting or scattering UV radiation. They are particularly useful for people who are sensitive to the ingredients found in other sunscreens. Sunblocks often contain one or more of these ingredients:
- Zinc oxide
- Titanium dioxide
- Iron oxide
Although past formulations were unsightly (often leaving a white film on the skin), newer "microfine" formulations are invisible after being applied. Microfine titanium dioxide is effective at protecting from both UVA and UVB rays.
Water resistance - Sunscreens are classified as "water-resistant" if they maintain their protection after two 20-minute immersions in water. They are classified as "waterproof" if they maintain their protection after four 20-minute immersions. You should seek a water-resistant or waterproof sunscreen if you will be participating in water sports, such as swimming or water skiing, or will be actively sweating.
However, independent testing has shown many products do not perform well in the real world. So it remains a good idea to apply sunscreen every time you leave the water, or frequently if you are actively sweating.
Using a Sunscreen
Sunscreen should be applied evenly and liberally on all sun-exposed skin within 30 minutes before going outside to give sunscreen time to take effect. (Sunblocks are effective immediately after being applied.) Sunscreens should be reapplied every two hours or following swimming or sweating to ensure effective sun protection. Apply sunscreen generously and reapply frequently at least every two hours.
The chemicals may lose effectiveness over time, so it is important to throw away sunscreen that is past its expiration date or is over two years old.
No sunscreen is 100% effective; take additional measures to avoid the damaging effects of the sun's rays.
Clothing
Clothing can provide excellent sun protection. However, not all clothing is protective. A thin, wet, white t-shirt will provide almost no protection from UV rays. When selecting clothes for sun protection, consider the following:
- Cover your head, shoulders, arms, legs, and feet.
- Use a hat that is broad-brimmed (brim should be at least four inches wide).
- Wear fabrics that are thicker or with a tight weave; these allow less sunlight to penetrate the skin.
- Wear darker-colored clothes that absorb more UV rays.
- Wear clothing made from nylon or Dacron because it is more protective than cotton.
- Avoid remaining in wet clothes because wet fabric may allow more UV rays to penetrate the skin.
- Wash clothing with chemical absorbers to increase their protectiveness.
- Some clothing comes with a UPF rating that stands for "Ultraviolet Protection Factor." This measures the ability of the fabric to block UV radiation from penetrating to the skin. A fabric with a UPF 15 allows only 1/15th (6.66%) of the UV radiation to penetrate your skin as compared to uncovered skin.
Garments fall into 3 categories:
- Good protection: UPF = 15 to 24
- Very good protection: UPF = 25 to 39
- Excellent protection: UPF = 40 to 50+
Choose clothing with a UPF rating of at least 15. Keep in mind that the UPF of a garment will decrease over time as the fabric wears.
Sunglasses
Overexposure to sunlight can cause cataracts and macular degeneration, a major cause of blindness. Sunglasses can provide effective sun protection for your eyes. However, not all sunglasses are of value. A darker lens itself does not guarantee protection. Look at the label to ensure that the glasses provide UV protection. Sunglasses should be large enough to shield your eyes from many angles. Look for sunglasses that are described as blocking 99% or 100% of UVA and UVB. The glasses may also be described as providing UV absorption up to 400 nm.
Shade
If possible, remain in the shade when outdoors. Keep in mind that shade does not provide full sun protection because UV rays can bounce off reflective surfaces, such as sand, snow, water, concrete, or even porch decks. In addition, some fabrics used as shade devices, such as parasols or umbrellas, may not provide sufficient sun protection. If you seek shade under a cloth, look for a fabric that is thick, tightly woven, and dark-colored.
Clear window glass provides protection from UVC and UVB, but not UVA rays. If you are frequently exposed to sunlight while driving, the plastic interleaf of your windshield (which prevents it from shattering) can help block the light, but side windows have no such protection. Non-drivers can make use of additional window shade devices for sun protection. Drivers in some states may be able to use darkly-tinted glass in the side windows, but this is illegal in some states.
Sun Protection Summary
- Avoid the sun when its UV rays are strongest, between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 15 or greater. Apply it 30 minutes prior to being exposed to the sun and reapply every two hours. Consider using a water-resistant sunscreen if you will be active (sweating) or in the water.
- Use a sunblock on your lips.
- Wear a broad-brimmed hat when outdoors.
- Wear sunglasses.
- Wear tightly woven, dark clothing to cover your arms, legs, and feet.
- Stay in the shade when possible.
- Avoid reflective surfaces, such as water or snow.
- Avoid sunbathing.
- Don't be fooled by cloudy days since damaging rays can penetrate clouds.
Source: Vivacare
Last updated : 1/29/2019