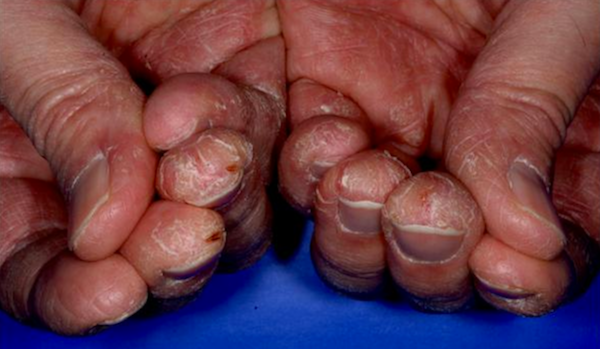
 Hand dermatitis is a general term describing inflammation of the skin of the hands Any type of dermatitis that develops on the hands can be classified as “hand dermatitis".
Hand dermatitis is a general term describing inflammation of the skin of the hands Any type of dermatitis that develops on the hands can be classified as “hand dermatitis".
Hand dermatitis is a common subset of eczema that may account for 80% of all job-related skin conditions. This is due to the hands being exposed to a variety of chemicals in the workplace that may irritate the skin or trigger an allergic reaction.
Although common, hand dermatitis is categorized separately because it may require a unique approach to evaluation and treatment.
Symptoms may range from mild to severe and include the following:
- dry chapped skin
- red, scaly and itchy patches of skin
- blisters or weeping areas.
- painful cracked skin
- deformed fingernails (may occur with long-standing hand dermatitis)
Without proper treatment, hand dermatitis symptoms can worsen and become chronic. Hand dermatitis can interfere with tasks and diminish one’s quality of life.
Causes of Hand Dermatitis
Irritatants. Even mild substances can irritate the skin. In fact water is a common cause of hand dermatitis because frequent hand washing can remove protective oils from the skin. Cleaning agents and other chemicals can also strip the skin of its oils, leading to dry, cracked skin.
Allergy. Allergic contact dermatitis is an allergic reaction to substances that come into contact with the skin. Certain allergens can trigger hand dermatitis, including nickel, Balsam of Peru, fragrances, rubber, food substances and topical vitamin E.
Hand Dermatitis Risk Factors
Having atopic dermatitis, asthma, or allergies increases a person's risk of developing hand dermatitis. When combined with frequent hand washing or even frequently immersing the hands in water or chemicals, the risk is even greater.
Certain work-related tasks increased the risk of developing hand dermatitis. Immersing one's hands in water several times a day, using cleaning agents or exposure to other chemicals can strip the skin of its protective barrier and lead to dermatitis. Occupations with high rates of hand dermatitis include nurses, hair stylists/bartenders, chefs/caterers/dishwashers, mechanics, painters and metalworkers.
Other factors that can trigger or worsen hand dermatitis includes stress, cold air, dry air (low humidity), and perspiration.
Diagnosis of Hand Dermatitis
In addition to a medical history and physical exam, the doctor may perform additional tests to diagnose hand dermatitis and determine the underlying cause.
Patch testing involves applying suspected allergens on the skin and monitoring the reaction.
Skin scraping and culture allows the doctor to examine skin under the microscope or determine if there is an underlying fungal skin infection.
Treatment of Hand Dermatitis
There are several treatment options available. A recommended treatment plan will be based on the possible cause, the severity of the dermatitis, its duration and response to past treatments.
Medications
- Topical corticosteroids help to reduce skin inflammation. These products are available in a variety of strengths. Due to the relatively thick skin on the hands, a moderate to very potent corticosteroid may be prescribed for short-term use.
- Calcineurin inhibitors provide a non-steroidal alternative to corticosteroids that also help to control inflammation.
- Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat an underlying bacterial infection.
- Botulinum toxin (Botox®) may be offered to those whose hands sweat excessively (palmar hyperhidrosis)
- Oral corticosteroids (prednisone) and immunosuppressants (cyclosporine, methotrexate, and mycophenolate mofetil) may be prescribed for severe cases of hand dermatitis that do not respond to other treatments.
Hand Dermatitis Prevention
- Apply moisturizers regularly. For best results, these should be applied after bathing and frequently throughout the day.
- Avoid known allergens. For example, if the patch test shows a nickel allergy, avoid wearing costume jewelry.
- Avoid irritants.
- Use gloves and change work habits. Wearing gloves can protect the skin from substances found in the workplace and while working around the home. A few days away from the job may clear a mild case. Changing a few habits can help keep the skin clear. Sometimes a material used to make the gloves causes hand dermatitis. For example, some medical professionals develop raw, inflamed hands after wearing latex gloves. Switching to a glove that does not contain latex usually brings relief.
Source: Vivacare
Last updated : 5/13/2022