While you may feel your symptoms are out of control, there is help for severe eczema in adults, teenagers and now in children 6 months of age and older.
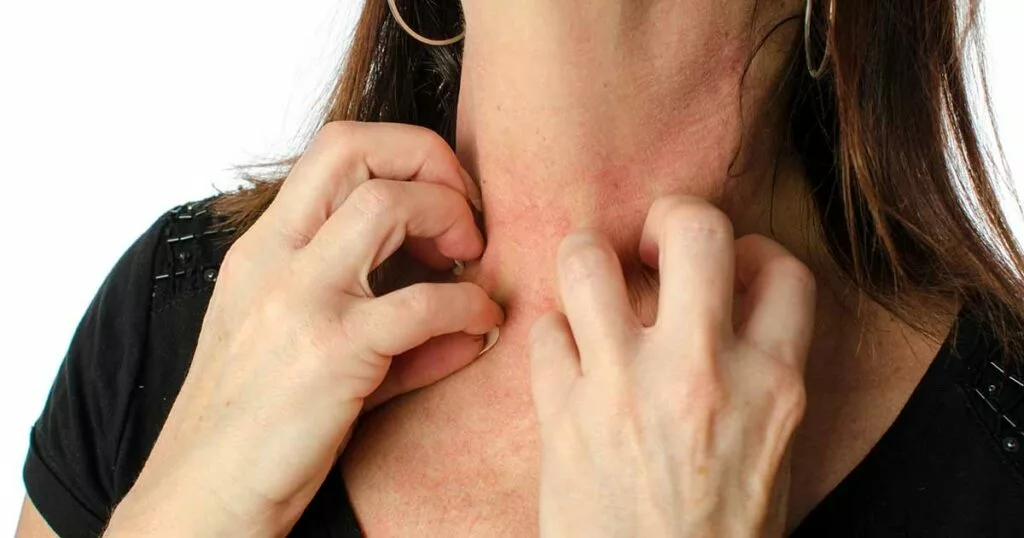 According to the National Eczema Association, there are four keys to eczema treatment:
According to the National Eczema Association, there are four keys to eczema treatment:
1. Know your triggers
Understand what triggers symptoms or makes your eczema worse. Avoid triggers when possible.
2. Develop a bathing and moisturizing routine
Bathe in lukewarm (not hot) water. Use gentle cleansers and avoid harsh soaps. Don’t allow your skin to fully dry before applying moisturizers and topical medications (if prescribed).
You may also want to consider wet wrap therapy. This involves placing moisturizer on the affected skin after the bath and then wrapping your skin in a warm, damp cloth or gauze. You can put light cotton clothing on over the wraps. And you can leave this on from two hours to overnight. This relieves inflammation and reduces itching. It helps reduce the need for medication, protects the skin and promotes healing. Wet wrap therapy can provide a lasting benefit.
3. Use over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications as directed
Your healthcare provider may advise you use both OTC and prescription medications to help control your symptoms. This may include pain medicine, topical ointments, creams or lotions, pills to reduce inflammation, or biologic medications. It is important to work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan to help manage symptoms.
4. Monitor your skin for signs and symptoms of infection
Skin infections are a serious risk associated with eczema. Part of treatment is monitoring your skin for signs of an infection. These signs may include:
- increased redness or purplish skin
- warm or hot skin
- swelling
- pain
- discharge
- fever
For any signs of infection, contact your healthcare provider right away to determine the correct treatment.
How is severe eczema treated in babies and toddlers?
For severe eczema in babies and toddlers, treatment is similar – identifying triggers, bathing and moisturizing. OTC and prescription treatments are more limited in young children and infants.
A biologic medication called dupilumab was recently approved for children ages 6 months and older with moderate to severe eczema.
What biologics are available for severe eczema?
Biologic medications are now used in the treatment of various diseases from breast cancer to diabetes to autoimmune conditions. And they are now being used in the treatment of moderate to severe eczema as well.
Biologics are made from living organisms such as humans, animals, plants, fungi, or microbes. They work by targeting specific immune cells that cause inflammation, leading to disease suppression or remission.Dupilumab is the first biologic approved for treating eczema. Tralokinumab is another biologic approved for eczema.
What are JAK inhibitors for severe eczema?
JAK inhibitors are small molecule medications. They help block the immune system’s response to reduce eczema severity. JAK inhibitors have been approved for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.
Abrocitinib and upadacitinib are two JAK inhibitor medications approved for eczema. Baricitinib is another JAK inhibitor awaiting FDA review.
- JAK inhibitors are approved for adults and children ages 12 and older with mild, moderate or severe atopic dermatitis.
- The medication blocks off an overactive pathway of enzymes. It limits the production of immune messengers called cytokines that can cause eczema symptoms.
- JAK inhibitors promote clear or almost-clear skin. They can relieve itching and inflammation and reduce skin thickness and scaling.
- Medication side effects may include mild nausea, nasal swelling, cough, headaches and high blood pressure.
- JAK inhibitors alter the immune system’s ability to react to germs, which can put patients at risk for bacterial, fungal and viral infections and/or certain cancers.
- FDA requires product warnings on JAK inhibitors about increased risk of serious heart-related events and blood clots.
- JAK inhibitors are expensive, but they are usually covered by insurance.
What is phototherapy (light therapy) for severe eczema?
Phototherapy, also called light therapy, is an in-office medical procedure conducted by either an allergist or dermatologist. It involves exposing the skin affected by eczema to ultraviolet (UV) light. A special light machine is used to deliver targeted bands of UV light. The amount of light exposure is timed and increased as treatment progresses.
Phototherapy can help reduce inflammation, relieve itching and boost the body’s ability to fight bacteria. It can be used in specific areas that aren’t responding to other treatments, or over the entire body if needed.
Side effects include sunburn, skin that appears to age rapidly, hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin) in people of color, and possibly skin cancer.
Nearly 70 percent of patients who are treated with phototherapy have positive results, but it is important to note that this treatment is not for everybody. Phototherapy is considered a second-line treatment for severe eczema and is used only for patients who have not had success with other measures.
How does moderate to severe eczema impact mental health?
People often underestimate how much eczema can impact a person’s mental health and affect quality of life. Eczema is more than just a physical symptom. Many people with eczema suffer from anxiety and depression. They tend to avoid social interaction, isolate themselves, and avoid taking part in activities because of their skin appearance. Constant itchiness, oozing rashes and blisters can affect a person’s mood, spirit and resilience.
If you or a loved one is struggling with mental health due to eczema, seek help from a mental health professional. Talk with your doctor and ask for a referral if needed. You can learn strategies to help you cope with eczema and lead a full and active life.
Some people may experience suicidal thoughts due to eczema. If you or someone you know struggles with thoughts of suicide, please get help right away. Talk to a mental health specialist or call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 800-273-8255.
Can I use prednisone for severe eczema?
Prednisone is an oral corticosteroid and it is not typically prescribed for eczema. In rare cases, it may be prescribed to treat severe eczema flare-ups. This is normally done for a short period of time. Long-term use of prednisone poses health risks including glaucoma or cataracts, elevated blood sugars, thin bones, increased risk of infection, and skin thinning.
© 2021 Allergy and Asthma Network

Last updated : 2/6/2023