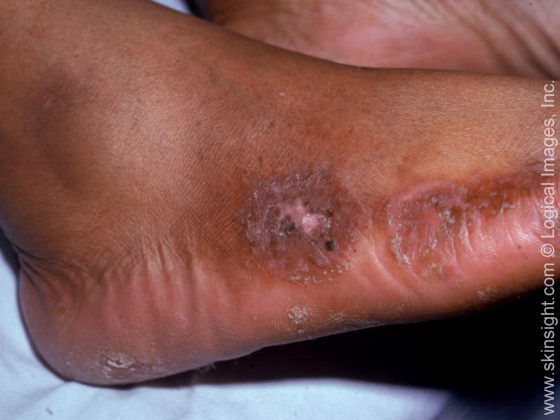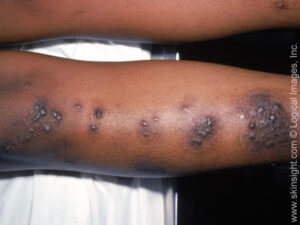
case of nummular dermatitis.
Nummular eczema, also called discoid eczema, describes itchy oval-shaped patches of inflamed skin.
The rash can arise on any part of the body, but is particularly common on the lower legs. The rash may persist for weeks or months before improving. Nummular eczema has a tendency to return again to the same location.
Nummular eczema is associated with dry skin and tends to worsen in the winter, or following exposure to wool, detergents, fabric softeners, rough clothing, and excessive bathing.
Treatment for Nummular Eczema
Nummular eczema cannot be cured, but it can be controlled.
Treatment is focused on the relief of itching. Depending on the location, severity, and duration of the rash, your physician may prescribe a topical corticosteroid, antihistamine, or coal tar. Additional treatments options are available for severe cases.
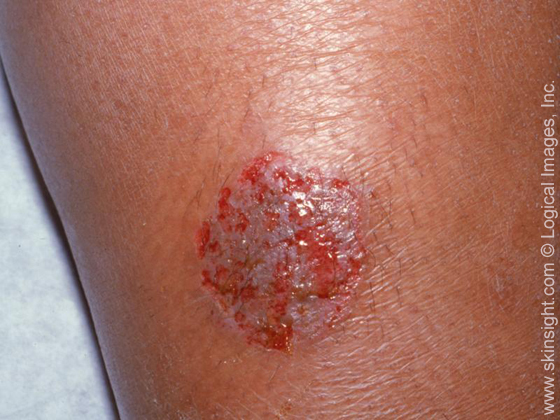
has been eroded by scratching, typical of
nummular dermatitis.
Skin infections, particularly by “staph" bacteria, are a common complication of nummular eczema and may be treated with topical or oral antibiotics.
Caring for Nummular Eczema
It is important to keep your skin moisturized. Bathing or showering in lukewarm water, quickly followed by the application of a thick moisturizer, such a Vaseline®, can prevent the skin from becoming excessively dry. Use a moisturizing soap, such as Cetaphil® or Dove®, and limit use of soap to the face, armpits, genital area, and feet.
People with nummular eczema may also benefit by avoiding woolen or rough clothing and washing clothes with dye free, fragrance free detergent without a fabric softener.
Source: Vivacare
Last updated : 5/13/2022