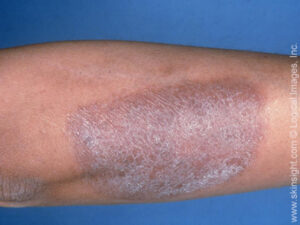
lichen simplex chronicus.
Lichen simplex chronicus is a skin disorder that leads to constant itching and scratching. Itching can be intense and increase during times of stress.
Lichen simplex chronicus occurs most commonly in people who have other skin disorders, such as atopic dermatitis or psoriasis, or have underlying anxiety. It also occurs children, who cannot stop scratching insect bites and other itchy skin conditions.
Parts of the body usually affected include the lower leg and ankle, forearm and wrist, neck, anal area, the back of the knee and inner elbow. The condition may come and go or change locations.
This skin disorder leads to a "scratch-itch cycle". It may begin with something that rubs, irritates, or scratches the skin, such as clothing. This causes the person to start rubbing or scratching the affected area. Constant scratching causes irritates the skin.....which leads to further itching.
The skin responds to constant scratching by developing thickened, scaly plaques that may appear darkened and leathery.
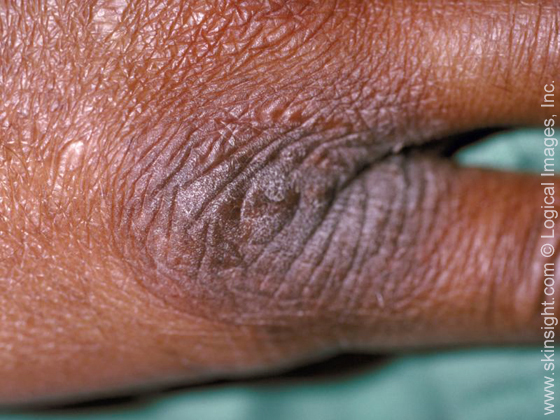
pronounced skin lines occur when
the skin is repeatedly rubbed.
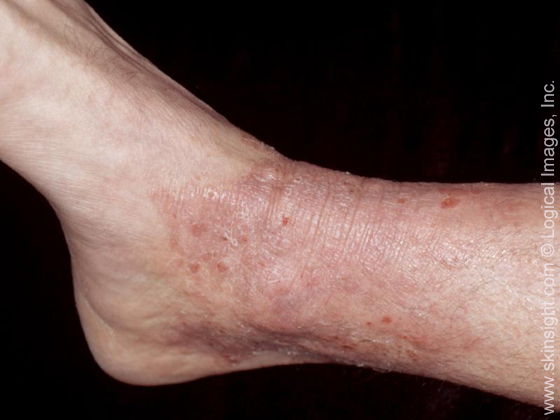
area leads to lichen simplex chronicus,
with thickened, rough, and sometimes red,
broken skin areas.
Scratching also damage the skin and result in a bacterial skin infection, such as cellulitis, or permanent scarring.
Treatment of Lichen Simplex Chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus can be treated by reducing the itch and controlling the scratching. An underlying skin condition, such as atopic dermatitis or psoriasis, will also need to be controlled.
The itching may be treated with a topical corticosteroid applied to the affected area of the skin.Antihistamines or sedatives may be prescribed to reduce itching and reduce scratching during sleep.
Wet dressings that moisturize, cover, and protect the area may be used with or without medication creams. They are left in place over thickened areas of skin for a week or more.
Those with signficant stress may benefit from the use of antidepressants.
Source: Vivacare
Last updated : 5/13/2022